International Futures Help System
IFs Knowledge Indices
The capacity of a society to tap from and add to the pool of existing knowledge, local and global, depends on
- skills and qualifications of people to assimilate existing and new knowledge,
- an innovation system to facilitate development or adoption of of new knowledge, processes and products
- a technological infrastructure to share, disseminate and regenerate knowledge and information within and across societies
- political and institutional environment conducive to the generation, diffusion and utilization of knowledge
- regulations that offer appropriate incentives towards and remove barriers from international transfer of knowledge
The above list of the driving dimensions of a knowledge system is exhaustive, to the best of our knowledge. The list has five dimensions contrasted to the four pillars identified by the WB KAM. However, World Bank includes tariff & non-tariff barriers, an indicator of international transfer, in their fourth pillar on economic and institutional environment.
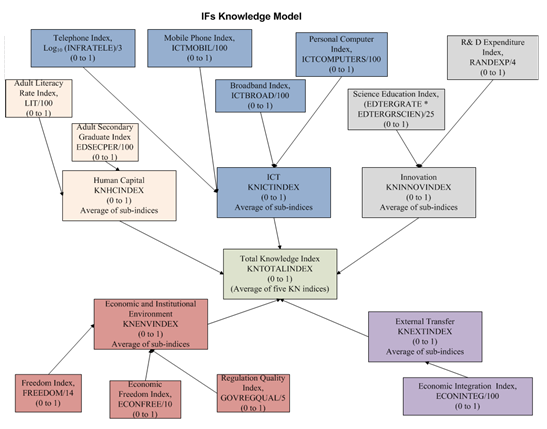
IFs now has five indices representing the five dimensions described above. The details of each of these indices, and a sixth one averaged from these five, will be described later. Suffice here to say that, the indices are calculated each of the forecast years by averaging the forecasted value of relevant IFs variables, normalized over a continuous interval going from 0 to 1. That is, IFs integrated simulation, first, forecasts a specific variable, e.g., adult literacy rate, it then converts the forecast to a normalized value lying between zero to one and then averages one or more of these normalized values to obtain an index along each of the dimensions of knowledge assessment. The table below compares IFs knowledge indices with those from World Bank.
| No. | Dimension/Pillar | World Bank Variables | IFs Index | IFs Variables |
| 1 | Human Capital | Adult literacy rate; Secondary enrollment rate; Tertiary enrollment rate | KNHCINDEX | Adult literacy rate; Adult secondary graduation rate |
| 2 | Innovation | R&D researchers, Patent count; Journal articles (all per million people) | KNINNOVINDEX | Total R&D expenditure (% of GDP); Tertiary graduation rate in science and engineering |
| 3 | ICT | Telephones (land + mobile) per 1000 persons; Computers per 1000 persons; Internet users per 10000 persons | KNICTINDEX | Telephone (fixed); Mobile phone; Personal Computers; Broadband |
| 4 | Economic and Institutional Regime | Tariff and non-tariff barriers; Regulatory quality; Rule of law | KNENVINDEX | Freedom; Economic freedom; Government regulation quality |
| 5 | International Transfer of Knowledge | KNEXTINDEX | Economic integration index | |
| 6 | Composite Index | Knowledge Index, KI (from the first three) and Knowledge Economy Index, KEI (from all 4) | KNTOTALINDEX | From all of the above |
 International Futures at the Pardee Center
International Futures at the Pardee Center